Introduction
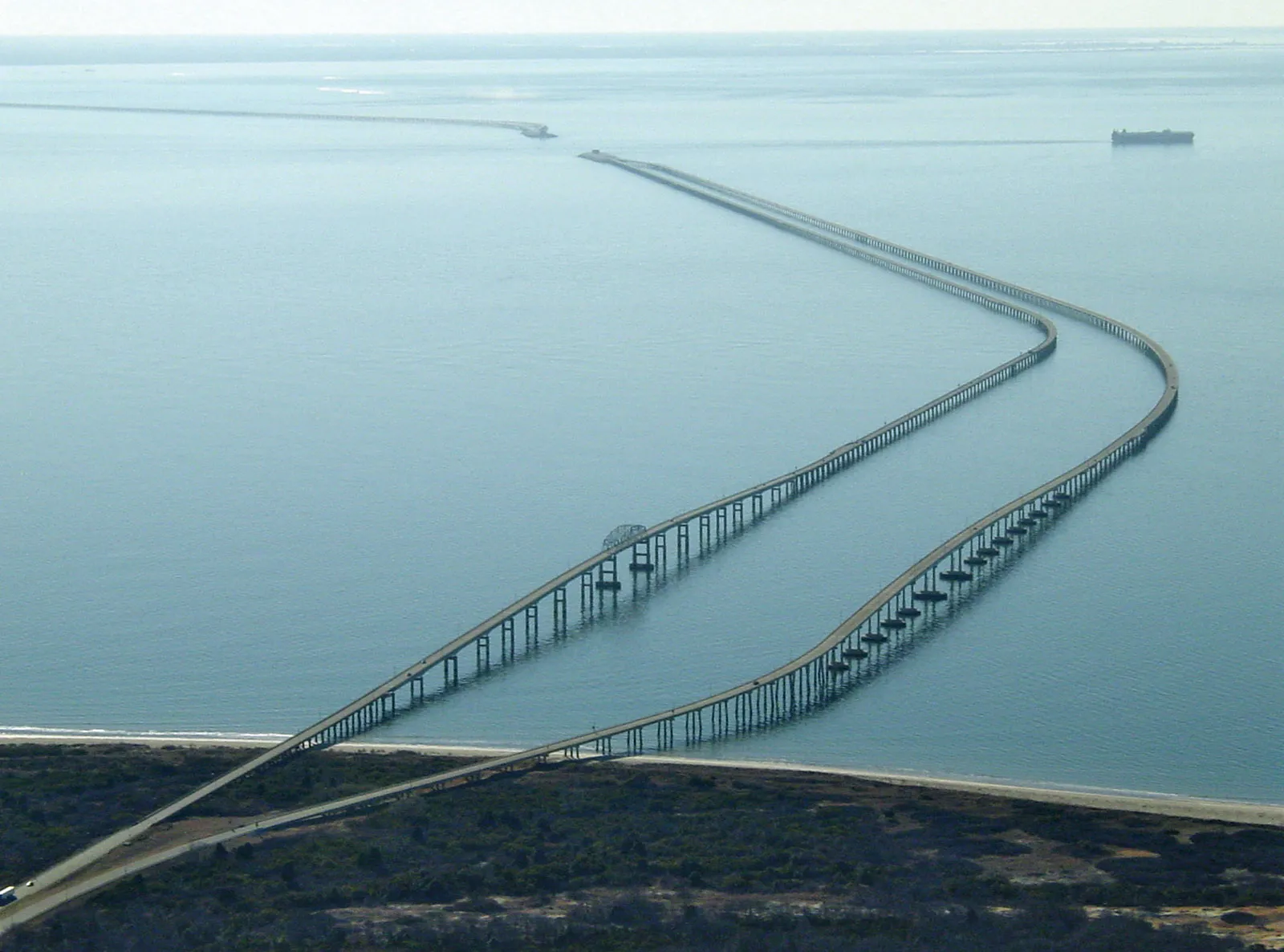
The Chesapeake Bay Bridge is not just a vital transportation link, but also an engineering marvel that connects Maryland’s Eastern and Western Shores. Spanning over 4.3 miles over the Chesapeake Bay, this bridge facilitates the movement of over 30 million vehicles annually. Its importance lies not only in transportation but also in tourism and economic development within the region.
Historical Significance
Constructed between 1956 and 1964, the Chesapeake Bay Bridge was a groundbreaking endeavor during its time, offering a faster and more efficient route than the previously required ferry service. Its construction was considered a significant achievement in engineering, utilizing over 24,000 tons of steel and affecting the lives of countless commuters. The bridge plays a critical role in connecting communities across the bay, promoting regional commerce and tourism.
Current Events and Developments
Recent developments around the Chesapeake Bay Bridge have sparked discussions regarding safety, maintenance, and the projected increase in vehicle traffic. Maryland Transportation Authority has announced-a $27 million maintenance project scheduled to commence next spring. This maintenance aims to enhance safety measures while preserving the structural integrity of the bridge. Moreover, planning is underway to conduct an environmental impact study to address concerns about ecological preservation in the surrounding areas, in response to community calls for sustainable transport practices.
Challenges and Future Prospects
One of the ongoing challenges faced by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge is managing the traffic congestion, especially during peak tourist seasons. The Maryland Transportation Authority is evaluating options such as implementing toll exemptions for certain drivers and introducing intelligent traffic management systems. Future enhancements may also include extending public transit options to reduce car reliance, which is becoming increasingly important in the context of climate change and sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion
The Chesapeake Bay Bridge remains an essential structure for Maryland and the broader Mid-Atlantic region, symbolizing connectivity and progress. As discussions about its maintenance and future improvements continue, the focus remains on balancing safety, accessibility, and environmental responsibility. For residents and tourists alike, the Chesapeake Bay Bridge will continue to be more than a passageway; it is a landmark that encapsulates the essence of regional identity and community.